Tired of feeling sluggish, no matter how much you eat? Or maybe you’re working out hard but not seeing the results you want?

The secret to unlocking your body’s full potential might be simpler than you think. It all starts with understanding the power of macronutrients – those essential building blocks that fuel your every move, thought, and bodily function.
- What are Macronutrients?
- Understanding Carbohydrates
- Functions of Carbohydrates in the Body
- The Glycemic Index (GI) and Its Importance
- Understanding Protein
- Recommended Daily Intake of Protein
- Balancing Macronutrients for Optimal Health
- How to Calculate Your Individual Macronutrient Needs
- Meal Planning and Recipe Ideas for Balanced Macronutrient Intake
- Focusing Only on Calories and Neglecting Macronutrient Balance
- Falling for Fad Diets and Misinformation About Macronutrients
What are Macronutrients?
Macronutrients – carbs, protein, and fats – aren’t just buzzwords in the health and fitness world. They’re the dynamic trio that provides your body with the energy it needs to thrive. From powering your workouts to repairing your muscles, macronutrients play a vital role in your overall health and well-being.
But with so much conflicting information out there, it’s easy to feel overwhelmed and confused. That’s where this ultimate guide comes in. We’ll break down the science behind macronutrients, debunk common myths, and equip you with the knowledge you need to make informed choices about your diet.

What You’ll Learn
By the end of this guide, you’ll:
- Gain a deep understanding of each macronutrient and its unique role in your body.
- Discover how to balance macronutrients for optimal health, whether your goal is weight loss, muscle gain, or simply feeling your best.
- Learn how to calculate your individual macronutrient needs and create a personalized nutrition plan.
- Feel empowered to make healthy food choices that support your fitness goals and overall well-being.
Are You Ready to Fuel Your Body for Success?
Dive into this comprehensive guide and unlock the secrets of macronutrients – the key to a healthier, happier, and more energized you!
Understanding Carbohydrates

Carbohydrates, often demonized in today’s diet culture, are actually the unsung heroes of energy production. They are your body’s primary fuel source, providing the energy you need to power through workouts, conquer your to-do list, and even fuel your brainpower. Let’s delve deeper into what carbohydrates are, their diverse forms, and their essential functions in the body.
What are Carbohydrates?
Carbohydrates are a type of macronutrient found in a wide array of foods, from fruits and vegetables to grains and legumes. They are composed of sugar molecules, which your body breaks down into glucose. Glucose is the primary source of energy for your cells, tissues, and organs
Carbohydrates come in different forms, each with its own unique characteristics and effects on your body. Understanding these distinctions is key to making informed choices about your carbohydrate intake.
Types of Carbohydrates
There are two main types of carbohydrates: simple and complex.
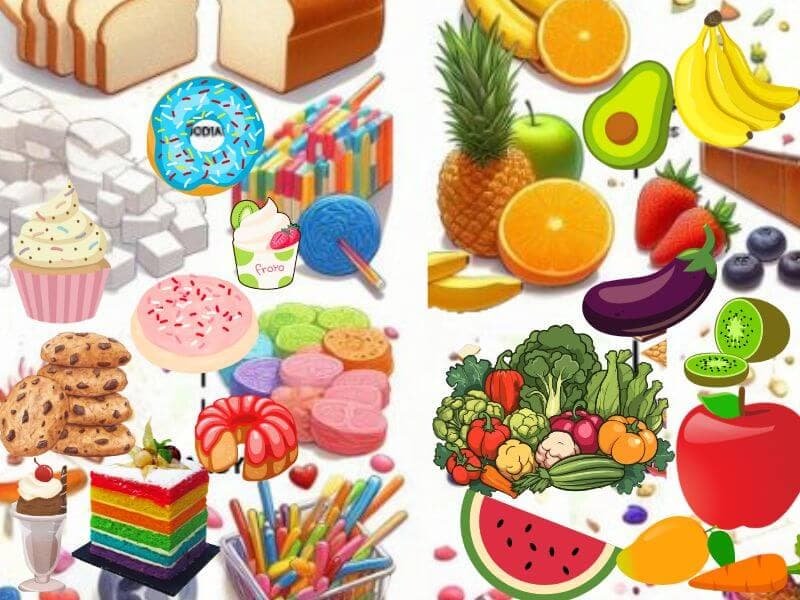

- Simple carbohydrates are made up of one or two sugar molecules and are quickly digested by the body. They provide a rapid burst of energy but can also lead to spikes in blood sugar levels. Examples of simple carbohydrates include table sugar, honey, fruit juice, and refined grains.
- Complex carbohydrates are composed of long chains of sugar molecules and take longer to digest. They provide sustained energy, keep you feeling fuller for longer, and are generally considered healthier than simple carbohydrates. Examples of complex carbohydrates include whole grains, legumes, and starchy vegetables.
Another important distinction is between refined and whole grains.
- Refined grains have been processed to remove the bran and germ, leaving only the endosperm. This process strips away valuable nutrients and fiber. Examples include white bread, white rice, and pastries.
- Whole grains contain all three parts of the grain kernel – bran, germ, and endosperm. They are a good source of fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Examples include brown rice, quinoa, and whole-wheat bread.
Functions of Carbohydrates in the Body
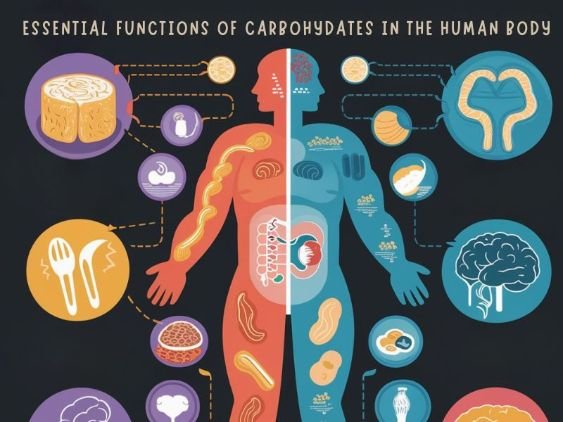
Carbohydrates play several crucial roles in your body:
- Energy source: Carbohydrates are the primary fuel for your body, providing energy for physical activity, brain function, and other bodily processes.
- Brain function: Glucose, the breakdown product of carbohydrates, is the preferred energy source for your brain. It’s essential for cognitive function, memory, and concentration.
- Fiber source: Complex carbohydrates, particularly whole grains, are rich in fiber. Fiber aids digestion promotes gut health, and can help regulate blood sugar levels.
Food Sources of Carbohydrates
You can find carbohydrates in a variety of foods, both healthy and less healthy:
- Fruits: Apples, bananas, berries, oranges, etc.
- Vegetables: Broccoli, carrots, spinach, potatoes, etc.
- Grains: Whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, oats, and whole-wheat bread.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, chickpeas, peas.
- Dairy products: Milk, yogurt (contain lactose, a type of sugar).
Choosing complex carbohydrates over simple carbohydrates and opting for whole grains over refined grains is key to a healthy diet.
Recommended Daily Intake of Carbohydrates
The recommended daily intake of carbohydrates varies depending on individual needs and activity levels. However, a general guideline is that 45-65% of your daily calories should come from carbohydrates. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to determine your specific needs.
The Glycemic Index (GI) and Its Importance
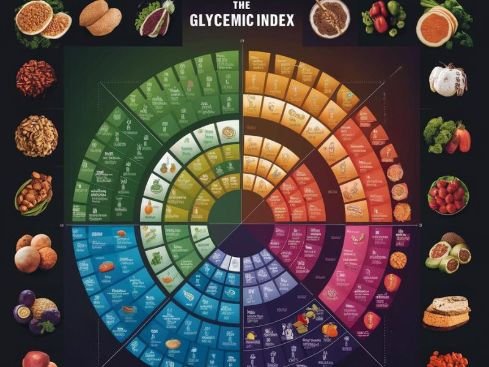
The glycemic index (GI) measures how quickly a food raises your blood sugar level. Foods with a high GI are quickly digested and cause a rapid spike in blood sugar, while foods with a low GI are digested more slowly and cause a gradual rise in blood sugar.
Choosing low-GI foods can help regulate blood sugar levels, prevent energy crashes, and promote satiety. This is especially important for individuals with diabetes or insulin resistance.
Common Myths About Carbohydrates
Despite their importance, carbohydrates are often misunderstood and demonized. Let’s debunk some common myths:
- Myth: All carbs are bad for you.
- Truth: Complex carbohydrates, especially from whole grains, are essential for health and provide sustained energy.
- Myth: Carbs make you fat.
- Truth: Weight gain is caused by consuming excess calories, regardless of the source. A balanced diet that includes carbohydrates can be part of a healthy weight management plan.
- Myth: Low-carb diets are the best way to lose weight.
- Truth: While low-carb diets can be effective for some people, they are not the only way to lose weight. A sustainable and balanced diet that includes carbohydrates is key.
Understanding Protein
Protein is often hailed as the king of macronutrients, and for good reason. It is essential for building and repairing tissues, producing enzymes and hormones, and supporting a wide range of bodily functions. Think of protein as the building blocks of your body, crucial for everything from strong muscles to healthy hair and nails. Let’s explore what protein is, its diverse roles, and how to incorporate it into your diet for optimal health and fitness.
What is Protein?

Protein is a complex macronutrient composed of smaller units called amino acids. There are 20 different amino acids, and your body needs all of them to function properly. However, it can only produce 11 of these amino acids on its own. The remaining nine, known as essential amino acids, must be obtained through your diet.
The Building Blocks of Protein: Amino Acids
Amino acids are the building blocks of protein, linked together in long chains to form complex protein structures. The specific sequence of amino acids determines the type of protein and its unique function in the body.
There are two main categories of amino acids:
- Essential amino acids: These nine amino acids cannot be synthesized by the body and must be obtained from food. They are essential for growth, development, and various bodily functions.
- Non-essential amino acids: These 11 amino acids can be produced by the body, so it’s not necessary to get them from your diet. However, they still play important roles in health and well-being.
Functions of Protein in the Body
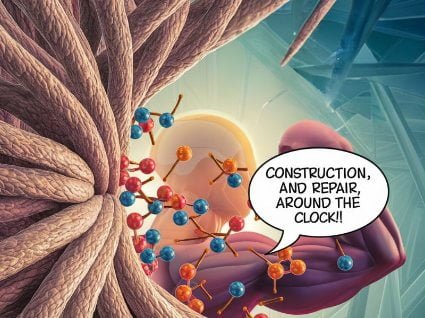
Protein is involved in virtually every aspect of your body’s functioning:
- Building and repairing tissues: Protein is essential for the growth and repair of muscles, bones, skin, and other tissues. It’s particularly important for athletes and those recovering from injuries.
- Enzyme production: Enzymes are proteins that facilitate chemical reactions in the body, including digestion, metabolism, and energy production.
- Hormone production: Many hormones, including insulin, growth hormone, and thyroid hormone, are made of protein. They regulate various bodily functions, from blood sugar control to growth and development.
- Immune function: Antibodies, the proteins that fight off infections, are made of protein. A sufficient protein intake is crucial for a healthy immune system.
- Transport and storage: Some proteins help transport molecules throughout the body, such as hemoglobin, which carries oxygen in the blood.
Food Sources of Protein
Protein is found in both animal and plant-based foods:
- Animal sources: Meat, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy products. These are considered complete proteins because they contain all nine essential amino acids.
- Plant sources: Legumes (beans, lentils, chickpeas), nuts, seeds, quinoa, tofu, tempeh. These are often incomplete proteins, meaning they lack one or more essential amino acids. However, by combining different plant-based protein sources throughout the day, you can ensure you get all the essential amino acids your body needs.
Recommended Daily Intake of Protein

The recommended daily intake of protein varies depending on factors like age, sex, activity level, and overall health. However, a general guideline is to aim for 0.8 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight. Athletes and those engaging in regular strength training may need more protein to support muscle growth and repair.
It’s important to note that protein needs can be met through a balanced diet that includes both animal and plant-based sources. There is no need to rely solely on protein supplements unless recommended by a healthcare professional or registered dietitian.
Protein Quality: Complete vs. Incomplete Proteins
As mentioned earlier, animal-based protein sources are considered complete proteins because they contain all nine essential amino acids in adequate amounts. Plant-based protein sources, on the other hand, are often incomplete proteins, meaning they are low in one or more essential amino acids.
However, you can easily get all the essential amino acids your body needs by combining different plant-based protein sources throughout the day. For example, combining rice and beans or hummus and pita bread creates a complete protein.
Common Myths About Protein

- Myth: You need to eat massive amounts of protein to build muscle.
- Truth: While protein is essential for muscle growth, excessive protein intake does not necessarily lead to greater muscle gains. Your body can only utilize a certain amount of protein at a time.
- Myth: Protein is only important for athletes and bodybuilders.
- Truth: Protein is crucial for everyone, regardless of activity level. It plays a vital role in maintaining healthy tissues, immune function, and overall well-being.
- Myth: Plant-based diets cannot provide enough protein.
Truth: With careful planning and a variety of plant-based protein sources, it’s entirely possible to meet your protein needs on a vegan or vegetarian diet.
Understanding Fats: Your Body’s Secret Weapon for Health & Vitality

Fats, often misunderstood and unfairly demonized, are essential players in your body’s intricate symphony of health. While the word “fat” might conjure images of weight gain and clogged arteries, the truth is far more nuanced. Fats are not only a valuable source of energy but also play a crucial role in hormone production, cell function, and even vitamin absorption. Let’s unravel the mysteries surrounding fats, explore their diverse types, and discover how to harness their power for optimal well-being.
What are Fats?
Fats, also known as lipids, are a type of macronutrient that your body needs for various functions. They are a concentrated source of energy, providing 9 calories per gram, compared to 4 calories per gram for carbohydrates and protein. This means that fats can provide long-lasting energy and help you feel fuller for longer periods.
However, not all fats are created equal. Understanding the different types of fats and their effects on your body is crucial for making informed choices about your diet.
Types of Fats

Fats can be classified into three main categories:
- Saturated Fats: These fats are typically solid at room temperature and are found primarily in animal products like meat, poultry, and dairy, as well as in some plant-based oils like coconut and palm oil. While your body needs some saturated fats for hormone production and other functions, excessive intake has been linked to increased LDL (“bad”) cholesterol levels and a higher risk of heart disease.
- Unsaturated Fats: These fats are typically liquid at room temperature and are considered the “healthy” fats. They are further divided into two categories:
- Monounsaturated Fats: Found in foods like olive oil, avocados, nuts, and seeds, these fats have been shown to help lower LDL cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Polyunsaturated Fats: Found in fatty fish, flaxseeds, walnuts, and sunflower oil, these fats are also beneficial for heart health and contain essential omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, which your body cannot produce on its own.
- Trans Fats: These are artificially created fats found in some processed foods and baked goods. Trans fats raise LDL cholesterol and lower HDL (“good”) cholesterol levels, making them the most harmful type of fat for heart health.
Functions of Fats in the Body
Fats play a multitude of vital roles in your body:
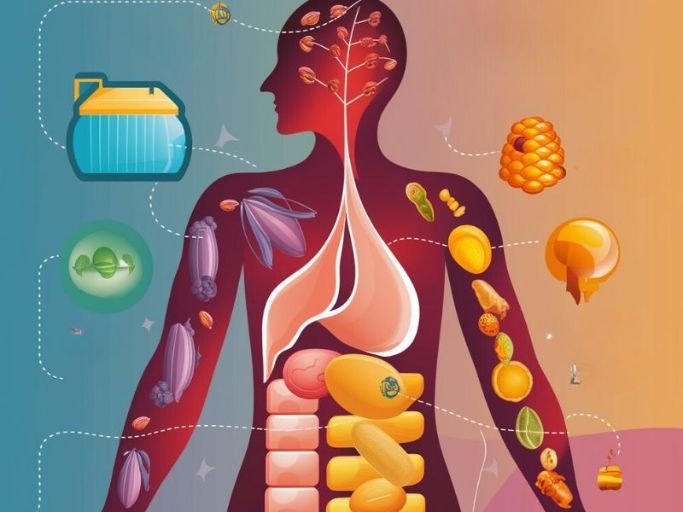
- Energy Storage: Fats serve as a concentrated source of energy, providing your body with fuel during periods of rest or low-intensity activity.
- Hormone Production: Fats are essential for the production of hormones, including sex hormones like estrogen and testosterone, which regulate various bodily functions.
- Cell Function: Fats are a key component of cell membranes, which help maintain cell structure and integrity.
- Vitamin Absorption: Fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K) require dietary fat to be absorbed and utilized by the body.
- Organ Protection: Fats surround and cushion your vital organs, protecting them from injury.
- Temperature Regulation: Fats help insulate your body, keeping you warm in cold temperatures.
Food Sources of Fats
You can find fats in a variety of foods:

- Oils: Olive oil, avocado oil, coconut oil, canola oil, etc.
- Nuts and seeds: Almonds, walnuts, flaxseeds, chia seeds, etc.
- Avocado: A creamy fruit packed with healthy monounsaturated fats.
- Fatty fish: Salmon, tuna, mackerel, sardines, etc.
- Dairy products: Butter, cheese, whole milk (contain saturated fats).
- Meat, poultry, and eggs: (contain saturated fats).
Recommended Daily Intake of Fats
The recommended daily intake of fats varies depending on individual needs and goals. However, a general guideline is that 20-35% of your daily calories should come from fats, with an emphasis on unsaturated fats over saturated and trans fats.
The Importance of Healthy Fats (Omega-3 and Omega-6 Fatty Acids)
Omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids are two types of polyunsaturated fats that are essential for health. Your body cannot produce these fats, so it’s important to get them through your diet.
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Found in fatty fish, flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts, these fats have anti-inflammatory properties, support heart health, and may benefit brain function.
- Omega-6 fatty acids: Found in vegetable oils, nuts, and seeds, these fats are also important for health, but excessive intake, especially relative to omega-3s, can promote inflammation.
Common Myths About Fats
Let’s debunk some common myths about fats:

- Myth: All fats are bad for you.
- Truth: Unsaturated fats are essential for health and can even help lower the risk of heart disease.
- Myth: Eating fat makes you fat.
- Truth: Weight gain is caused by consuming excess calories, regardless of the source. A balanced diet that includes healthy fats can be part of a healthy weight management plan.
- Myth: Low-fat diets are the best way to lose weight.
- Truth: While low-fat diets can be effective for some people, they are not the only way to lose weight. A sustainable and balanced diet that includes healthy fats is key.
Balancing Macronutrients for Optimal Health
Now that we’ve explored the individual roles of carbohydrates, protein, and fats, it’s time to delve into the art of balancing these macronutrients for optimal health and fitness. Achieving the right balance is crucial for reaching your goals, whether it’s shedding a few pounds, building lean muscle, or simply maintaining a healthy weight. Let’s uncover the secrets to macronutrient balance and how you can harness their power to fuel your body effectively.
Macronutrient Ratios for Different Goals
The ideal macronutrient ratio varies depending on your individual goals and needs. Here’s a general overview:

- Weight Loss: A common approach is a higher protein, moderate fat, and lower carbohydrate ratio. This can help increase satiety, preserve muscle mass, and promote fat burning.
- Muscle Gain: A slightly higher carbohydrate and protein intake is often recommended to fuel workouts, support muscle recovery, and promote muscle growth.
- Maintenance: A balanced macronutrient ratio that aligns with your individual needs and activity level is key to maintaining a healthy weight and body composition.
How to Calculate Your Individual Macronutrient Needs
Calculating your individual macronutrient needs can seem daunting, but it’s a crucial step in creating a personalized nutrition plan. Several factors come into play, including:
- Age: Your age influences your metabolic rate and energy requirements.
- Sex: Men and women have different body compositions and hormonal profiles, affecting their macronutrient needs.
- Weight: Your body weight is a key factor in determining your caloric and macronutrient needs.
- Height: Your height is also considered in calculating your basal metabolic rate (BMR), the number of calories your body burns at rest.
- Activity Level: Your activity level plays a significant role in determining your energy expenditure and macronutrient needs.
There are various online calculators and formulas available to help you estimate your individual macronutrient needs. However, for a more accurate and personalized approach, consulting with a registered dietitian is recommended.
Practical Tips for Tracking Macronutrients

Tracking your macronutrient intake can be a helpful tool for ensuring you’re meeting your nutritional goals. Here are some practical tips:
- Use a food diary or tracking app: These tools allow you to log your food intake and monitor your macronutrient breakdown.
- Weigh and measure your food: This is the most accurate way to track your intake, especially for protein and fats.
- Learn to eyeball portions: If weighing and measuring isn’t feasible, practice estimating portion sizes using your hand or common household objects.
- Focus on whole, unprocessed foods: These foods are naturally nutrient-dense and make it easier to track your macronutrients.
- Don’t stress about perfection: Aim for consistency over perfection and make adjustments as needed.
The Role of Macronutrients in Different Diets
Macronutrient ratios can vary significantly depending on the type of diet you follow:
- Vegan and vegetarian diets: These diets focus on plant-based foods and may require more attention to ensure adequate protein and iron intake.
- Ketogenic diet: This low-carb, high-fat diet emphasizes fats as the primary source of energy and restricts carbohydrates.
- Paleo diet: This diet focuses on whole, unprocessed foods that mimic what our hunter-gatherer ancestors ate, emphasizing protein and healthy fats.
- Mediterranean diet: This diet is rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats like olive oil, with moderate amounts of fish, poultry, and dairy.
Meal Planning and Recipe Ideas for Balanced Macronutrient Intake
Planning your meals in advance can help ensure you’re meeting your macronutrient goals while enjoying a variety of delicious and nutritious foods. Here are some tips:
- Choose a variety of protein sources: Include both animal and plant-based proteins throughout the week.
- Fill half your plate with vegetables: This will help you get plenty of fiber, vitamins, and minerals.
- Incorporate healthy fats: Add nuts, seeds, avocado, olive oil, or fatty fish to your meals.
- Choose complex carbohydrates: Opt for whole grains, legumes, and starchy vegetables over refined carbohydrates.
- Experiment with different recipes: Find recipes that fit your taste preferences and macronutrient goals.
By mastering the art of balancing macronutrients, you can unlock your body’s full potential, achieve your health and fitness goals, and enjoy a vibrant and fulfilling life.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them

Navigating the world of macronutrients can be tricky, and it’s easy to fall into common pitfalls that can hinder your progress towards your health and fitness goals. In this section, we’ll shed light on these common mistakes and provide you with practical strategies to avoid them, ensuring you’re on the right track to optimal nutrition.
Over-restricting or Eliminating Certain Macronutrients
One of the most prevalent mistakes is adopting a restrictive mindset towards macronutrients. Some diets demonize carbohydrates, while others vilify fats. However, each macronutrient plays a vital role in your body, and completely eliminating or drastically reducing any of them can lead to nutrient deficiencies and imbalances.
Instead of viewing macronutrients as the enemy, focus on achieving a balanced intake that aligns with your individual needs and goals. Embrace the diversity of food sources and enjoy a wide range of nutrient-dense options from all three macronutrient groups.
Focusing Only on Calories and Neglecting Macronutrient Balance

While calorie control is essential for weight management, solely focusing on calorie counting can be misleading. Two meals with the same calorie content can have vastly different macronutrient compositions and effects on your body. For example, a high-protein, low-carb meal will keep you feeling fuller for longer compared to a high-carb, low-protein meal.
Instead of obsessing over calories alone, shift your focus to achieving a balanced macronutrient intake. Prioritize whole, unprocessed foods that provide a good mix of carbohydrates, protein, and fats. This approach will not only help you manage your weight but also provide your body with the nutrients it needs to thrive.
Not Adjusting Macronutrient Ratios Based on Individual Needs and Goals
Your macronutrient needs are unique and depend on various factors, including your age, sex, activity level, and goals. A one-size-fits-all approach to macronutrient ratios won’t work for everyone. For example, an athlete training for a marathon will have different carbohydrate needs compared to someone trying to lose weight.
To optimize your nutrition, it’s crucial to tailor your macronutrient intake to your individual needs and goals. This might involve adjusting your protein intake based on your activity level or modifying your carbohydrate intake depending on your weight loss or muscle gain goals. Consider consulting a registered dietitian to help you determine the ideal macronutrient ratio for your specific situation.
Falling for Fad Diets and Misinformation About Macronutrients

The internet is rife with fad diets and misinformation about macronutrients. Some diets claim that eliminating entire food groups is the key to health and weight loss, while others promote extreme macronutrient ratios that are unsustainable and potentially harmful.
It’s crucial to approach nutrition information with a critical eye and rely on evidence-based sources. Consult with qualified healthcare professionals or registered dietitians for personalized guidance and steer clear of fad diets that promise quick fixes but lack scientific backing.
By avoiding these common mistakes and adopting a balanced and personalized approach to macronutrient intake, you can fuel your body for optimal health, fitness, and well-being. Remember, nutrition is not about restriction but about nourishing your body with the right balance of nutrients to support your unique needs and goals.
Conclusion

Congratulations! You’ve now completed your crash course in macronutrients, the essential building blocks of nutrition. By understanding the unique roles of carbohydrates, protein, and fats, you’re equipped to make informed choices about your diet and fuel your body for optimal health and fitness.
Remember, achieving a balanced macronutrient intake isn’t about restriction or deprivation. It’s about nourishing your body with a variety of whole, unprocessed foods that provide the energy, nutrients, and building blocks it needs to thrive. By experimenting with different macronutrient ratios and finding what works best for you, you can achieve your health and fitness goals while enjoying a sustainable and satisfying lifestyle.
Embrace the Power of Macronutrients and Fuel Your Journey to Optimal Health

Don’t let confusion or misinformation hold you back. Embrace the power of macronutrients and take control of your nutrition. Whether you’re aiming to lose weight, build muscle, or simply enhance your overall well-being, a balanced macronutrient intake is the key to unlocking your body’s full potential.
Additional Tips
- Share Your Journey: Have you experimented with macronutrient tracking? Share your experiences and insights in the comments below!
- Connect with a Registered Dietitian: If you’re seeking personalized guidance on macronutrients and nutrition, don’t hesitate to consult with a registered dietitian. They can help you create a customized plan that aligns with your individual needs and goals.
- Stay Informed: Subscribe to our blog for more evidence-based nutrition tips, delicious recipes, and inspiration to fuel your healthy lifestyle.

Remember, knowledge is power. By understanding macronutrients, you’re taking a significant step towards a healthier, happier, and more energized you. So, go ahead and fuel your body for success!




